What Is RAID Storage and How Does It Work?
RAID is a storage technology that utilizes multiple hardware disk units to improve performance, reliability and ease of access. Standard RAID levels use techniques such as disk mirroring, disk striping and error correction to achieve these benefits.
Rocket Yard explains the basics of RAID storage, including different levels, types of volumes and controllers. We will also explore the pros and cons of RAID storage to help you decide whether it is right for your digital workflow.
What is RAID?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a storage configuration that leverages multiple disk drives to improve performance, data redundancy and fault tolerance. There are many different RAID types and each offers unique benefits to your organization.
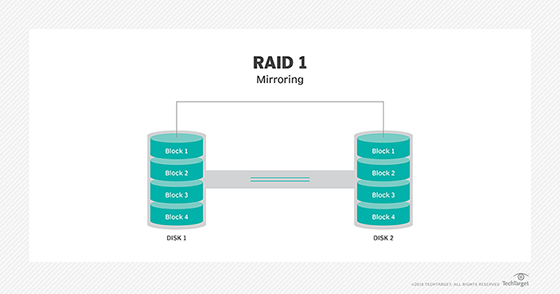
The most popular and widely used RAID level is RAID 1. It works by writing data to both a “data” drive and a “mirror” drive. This creates a redundant copy of your data and enables you to replace one failed drive without losing any information. Most RAID units also allow you to hot-swap a drive, meaning that you can swap out the faulty drive and reboot the system with no downtime.
Other RAID levels include striped sets and parity drives, each offering different advantages to your organization. For instance, striped sets can provide higher storage capacity than a single drive while parity drives can correct errors on your disks. RAID can be configured either through software or hardware controllers. The former requires the installation of a driver or firmware in your operating system or in the Option ROM of the hardware drive.
Although RAID renders company data more resilient and reliable, it is not a replacement for backups. Backups are the best way to protect against cyberthreats and natural disasters. In the event that your RAID array experiences a hardware failure, you will need to work with a RAID recovery specialist.
What are the Benefits of RAID?
RAID storage solutions are great for anyone who needs to edit video with a fast, reliable system. However, knowing what configurations are available is important to understand your specific video editing needs. Rocket Yard takes a look at the most common RAID levels and their benefits so you can determine what type of RAID solution is best for your project.
The primary benefit of RAID is data redundancy, but it also increases performance. For example, the most popular level, RAID 1, writes data across multiple disks, which improves read/write speeds as each drive is accessed in parallel. RAID also provides a high degree of fault tolerance, meaning that if one drive fails the other drives can reconstruct the lost information.
It’s important to note that RAID does not protect against human error or viruses, so it should never be used as a replacement for a comprehensive backup strategy. Additionally, a RAID array cannot prevent data corruption or file deletion if the drive is re-formatted or has its operating system replaced.
The drawback of RAID is that it requires multiple hard drives to function, which reduces the overall storage capacity. Additionally, since every single drive must store identical data it is very expensive compared to other hardware RAID setups. However, if you do lose data due to a hard drive failure or other issue it can be easily recovered by a professional RAID data recovery provider.
How Does RAID Work?
RAID is a technology that pools multiple drives together to appear as a single volume with higher performance and reliability than each drive individually. This is used to improve data read and write speeds or increase fault tolerance. RAID can be implemented in many different ways depending on the configuration chosen.
A RAID array can use one of three methods to pool storage: mirroring, striping, or parity. Each method has its own benefits. RAID levels 1 and 2 use mirroring to create identical copies of data on multiple drives, increasing both read speed and space efficiency. However, if any drive fails, all of the data becomes inaccessible.
RAID 5 uses disk striping and distributed parity to provide both performance and fault tolerance. This means that data is striped across all of the disks, and the parity information is calculated and stored on a separate drive. This provides improved read performance, but it also reduces the write speed.
RAID 6 is similar to 5, but it also includes dedicated parity, which allows it to withstand the loss of two disks without losing any data. This makes it more resilient to failures, but it does require more disks to function than 5. All RAID configurations can suffer from hardware failure, so it’s important to have a backup plan in case of an issue. If you do experience a problem, it’s best to work with a specialist in RAID data recovery that can help restore your information with minimal downtime.
What are the Drawbacks of RAID?
Although the technology of RAID has evolved to meet the needs of data storage, it is not without its drawbacks. As a result, it’s important to have backups in place to mitigate against the risk of data loss.
In addition, while RAID increases performance and redundancy, it can also degrade if one of the drives fails. This is because the array has to work out parity on the remaining drives, resulting in slower performance.
Another downside of RAID is that it can increase the risk of data loss if the system experiences hardware failure or power outage. This is because the drives used in a RAID configuration can fail – and even though spinners have gotten faster, they are still mechanical parts that can suffer from the same problems as any other hard disk drive.
The good news is that data recovery specialists can often recover data from a failed raid array with minimal loss. However, it’s important to choose a company that has experience with different RAID levels and knows how to address issues with the different types of redundancy. Also, make sure the company has direct partnerships with storage vendors and development capabilities to accommodate new or custom RAID configurations. Also, make sure the company offers a free diagnostic so you can get an idea of their capabilities before making a commitment.







